Bitumen viscosity grades
Paving bitumen has traditionally been specified in terms of penetration, but viscosity measurement offers a more precise way to specify binder consistency and a more efficient way to figure out the bitumen’s temperature susceptibility. There are two series of viscosity grade bitumen produced by the American Association of State Highway Officials (AASHTO). AC stands for asphalt cement, and it is followed by a figure that represents the viscosity in hundreds of poises at 60 degrees Celsius. After the bitumen has been aged, the second series is labeled AR (aged residue) and is followed by a number that indicates the viscosity in poises (not hundreds of poises) at 60 C.
The empirical penetration test was superseded by this scientific test as the primary method of characterizing asphalt binder. For more than 20 years, the US had achieved excellent outcomes from the viscosity grading system. Compared to the penetration grading system, the viscosity grading system makes more sense. The definition of viscosity is the opposite of fluidity. Thus, the bituminous material’s fluid quality is defined by its viscosity. Consistency is generally referred to as viscosity, which is a measurement of flow resistance. Many academics think that rather than using the traditional penetration units for bitumen grading, absolute viscosity should be used. The foundation of viscosity grading is a basic, scientific viscosity test that uses poise as its measuring unit and is carried out at 60˚C, or close to the summertime maximum pavement temperature. The viscosity grading system is based on the viscosity-temperature relationship, and the VG (Viscosity Grade) system is commonly used. These grades indicate the average viscosity of bitumen at a specific temperature.
Here’s what each grade signifies:

- VG10: This implies a bitumen viscosity grade where the average viscosity at 135°C is 1 poise. VG10 bitumen is relatively softer compared to higher viscosity grades.
- VG20: The average viscosity of bitumen at 135°C is 2 poise. VG20 bitumen is slightly more viscous than VG10 but still falls into the category of medium-soft bitumen.
- VG30: VG30 signifies a bitumen grade with an average viscosity of 3 poise at 135°C. This grade is commonly used for various road construction applications.
- VG40: VG40 indicates a bitumen viscosity grade where the average viscosity at 135°C is 4 poise. VG40 is relatively harder compared to lower viscosity grades and is suitable for specific road construction requirements.
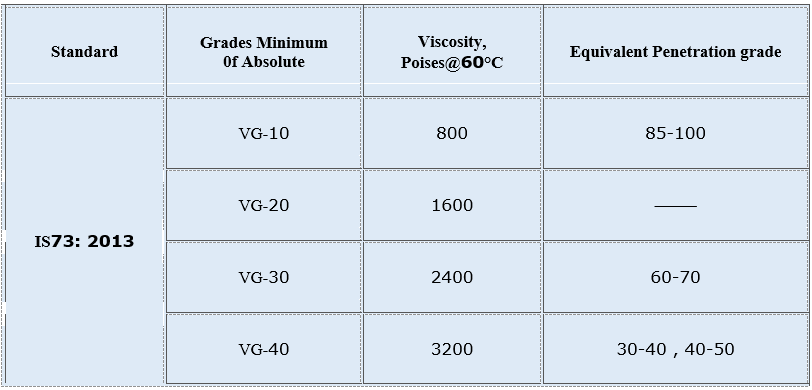
These viscosity grades are used to classify bitumen based on its stiffness and flow characteristics, allowing engineers and construction professionals to select the appropriate grade for specific applications. The choice of bitumen grade depends on factors such as climate, traffic conditions, and specific engineering requirements. Different viscosity grades are designed to perform optimally under varying temperature and traffic conditions.
Specifications
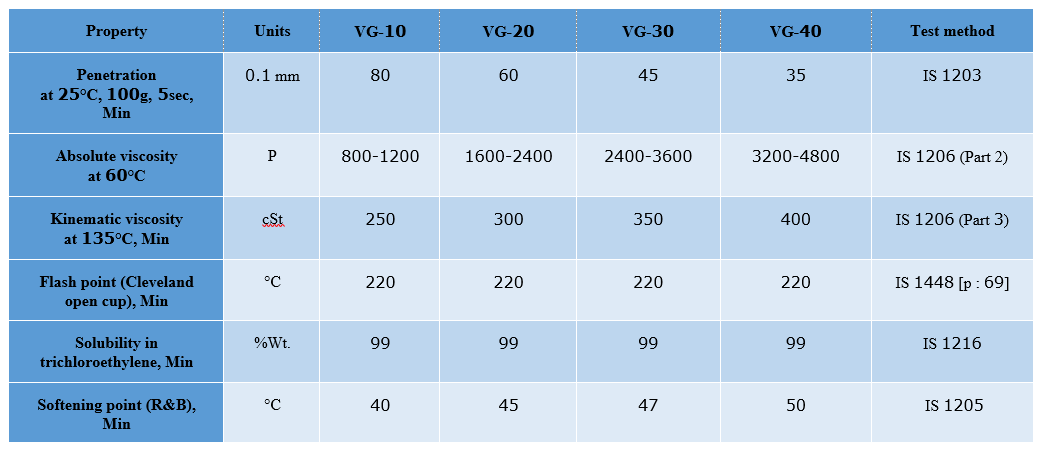
Tadbir Tejarat Company is ready to supply all kinds of bitumen, including VG10, VG20, VG30, VG40 grades of bitumen.
